Exploring the costs and benefits of two alternative investment approaches
SYNOPSIS
Proponents of active and passive investment management styles have made exhaustive and valid arguments for and against both approaches. Each has its merits and inherent drawbacks, and this paper will not endorse one style over the other. Rather, our goal is to define the characteristics of each approach in an effort to help you determine which best suits your needs and preferences.

Investors encounter different opportunities and challenges at different times, which can help determine the investment management approach that is the best for them. On one hand, we believe active management can add value when coupled with strict due diligence services. On the other hand, when limited investment options are available or the best you can do is “average” performance, passive investment options may make more sense due to fees and other considerations. Regardless, a clearer understanding of how to balance and leverage both active and passive management is crucial to realizing your investment objectives.
The Basics of Active and Passive Management
The proliferation of passive management strategies in recent years is well documented and evidenced by the exponential growth of the Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) marketplace. Currently there are more than 1,000 ETFs available; many of these employ passive strategies and range from those replicating the widely recognized S&P 500 Index to more niche indexes such as the S&P Global Water Index. Passive management has proven a viable strategy and is challenging the more traditional portfolio construction practice of investing strictly in active managers.
Several factors should be considered when deciding between active and passive management. These factors vary greatly from one client to another and the solutions can be just as unique, ranging from a purely passive to purely active approach or some combination of both. The correct use of these strategies can help build a portfolio better suited to your specific needs.
Active vs. Passive Management Defined
The difference between active and passive investment management lies primarily in the stated goal and the approach used to reach it.Active management is overseen by investment professionals striving to outperform specific benchmarks. Passive management (i.e., index ETFs, index funds) attempts to replicate the return pattern of a specific benchmark. With active management, investment experts are hired based on the perceived value they can add above and beyond the benchmark. Passive management often stresses low costs, tax efficiency and the concept of market efficiency.
As Table 1 shows, there are tradeoffs between the costs and potential benefits of the two approaches.
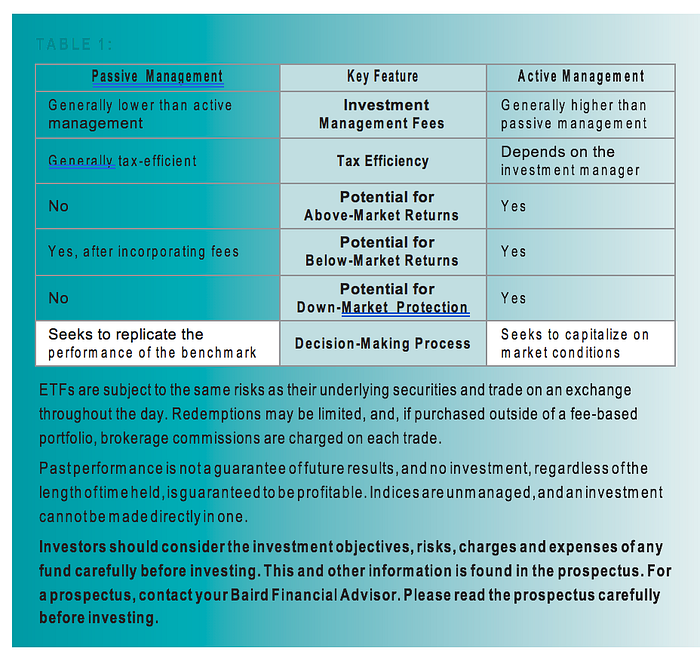
Passive management will maintain exposure to the market, but not offer any potential for above-benchmark returns (or down-market protection). Active management offers the potential for above-market returns, but comes with the chance that the manager won’t beat the stated benchmark. Also, neither approach can completely shelter you from the possibility of below-market returns. These variables and the nuances of your specific situation make this a decision best made with the assistance of your Financial Advisor. The remainder of this paper should help guide you through that decision-making process by offering examples of when, where and how Baird believes active or passive strategies should be used. Implementation of Active and Passive Strategies
Proceeding from the conclusion that both active and passive management are valid strategies, the question becomes where and when is one more appropriate than the other? The following pages will outline several common considerations…



